Gone are the days of data silos, and now systems rarely work in isolation. Businesses rely on CRMs, ERPs, eCommerce platforms, data warehouses, and more and all of which need to stay in sync.
Middleware integration tools are the one-word answer to all the data integration hassles, as they enable smooth data exchange between systems, supporting reliable communication and real-time processing. The right integration middleware doesn’t just connect various applications, it improves speed, reduces errors, and scales with your enterprise.
In this blog, delve more into middleware tools, and a list of seven recommended middleware integration tools for seamless data connectivity.
What Are Middleware Integration Tools?
Middleware integration tools work as a communication bridge between different software applications. In simple words, these tools enable seamless data exchange by connecting systems, whether cloud-based, on-premise, or hybrid, which means they can work together in real-time.
To avoid building custom connectors for every application, middleware tools provide reusable components and prebuilt connectors, which support APIs, messaging queues, data mapping, and transformation features to ensure data flows correctly from one system to another.
Whether syncing your CRM with your ERP or automating workflows across departments, middleware tools help build scalable and reliable integrations without coding everything from scratch. They reduce manual processes, eliminate data silos, and create unified workflows across departments or platforms.
Below is the list of the top 8 Middleware Integration Tools for seamless Data Connectivity curated by our in-house industry experts:
- DCKAP Integrator
- Workato
- Boomi
- Mulesoft Anypoint Platform
- Jitterbit
- IBM App Connect
- Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
- Informatica
How These Tools Made It into This List
Now, let’s understand why these middleware integration tools were featured in the list. The list depicts a detailed review of each tool’s capabilities, business value, and real-world usage. Here are the criteria that we considered while shortlisting the top 8 middleware integration platforms:
- Integration versatility: Support for cloud, on-premise, and hybrid deployments
- Ease of implementation: Low-code/no-code interfaces for faster setup
- Performance and reliability: Stable uptime, error handling, and secure data exchange
- Connector library: Prebuilt connectors for common business apps and services
- Scalability: Ability to handle growing integration needs
- User trust: Positive customer reviews and strong market presence
Top 7 Tools for Middleware Integration
1. DCKAP Integrator
Overview: DCKAP Integrator from DCKAP Technologies is a cloud-based middleware solution built for distributors, manufacturers, and retailers. It simplifies enterprise application integration across ERP, CRM, and eCommerce systems. Supporting robust data exchange, it offers ready-to-deploy/ use connectors for Epicor, Salesforce, Magento, BigCommerce, and Shopify. This integration middleware automates order syncing, inventory updates, and customer data flow, streamlining business operations for increased efficiency. Designed with a no-code interface, users can manage integrations with zero coding.
The platform also offers dashboards for operational visibility, error tracking, and performance metrics, making it easier to maintain integration health.
Advantages
- No-code, drag-and-drop interface.
- Native connectors for ERP, eCommerce, and CRM.
- Real-time data exchange for inventory and orders.
- Customized onboarding for B2B businesses.
Disadvantages
- May need more time to implement for tools not used by manufacturers or distributors
Best Suited For: Distributors and manufacturers seeking easy ERP and eCommerce connectivity without deep development resources.
2. Workato
Overview: Workato merges integration middleware with RPA, giving businesses a unified automation platform. Its no-code “recipes” let teams build workflows in simple steps. It connects SaaS, APIs, databases, and even AI tools without writing code. Workato enables IT and business teams to collaborate on automating business operations across systems in real-time. It also provides advanced features like conditional logic, multi-step workflows, and version control for enterprise-grade automation.
Advantages
- No-code interface.
- 1,000+ ready connectors.
- Combines RPA + iPaaS.
- Ideal for cross-functional automation.
Disadvantages
- Costly at higher usage.
- Complex logic still needs technical input.
- Limited support for offline use.
Best Suited For: Teams seeking to empower non-tech users and integrate various applications through simple automation flows.
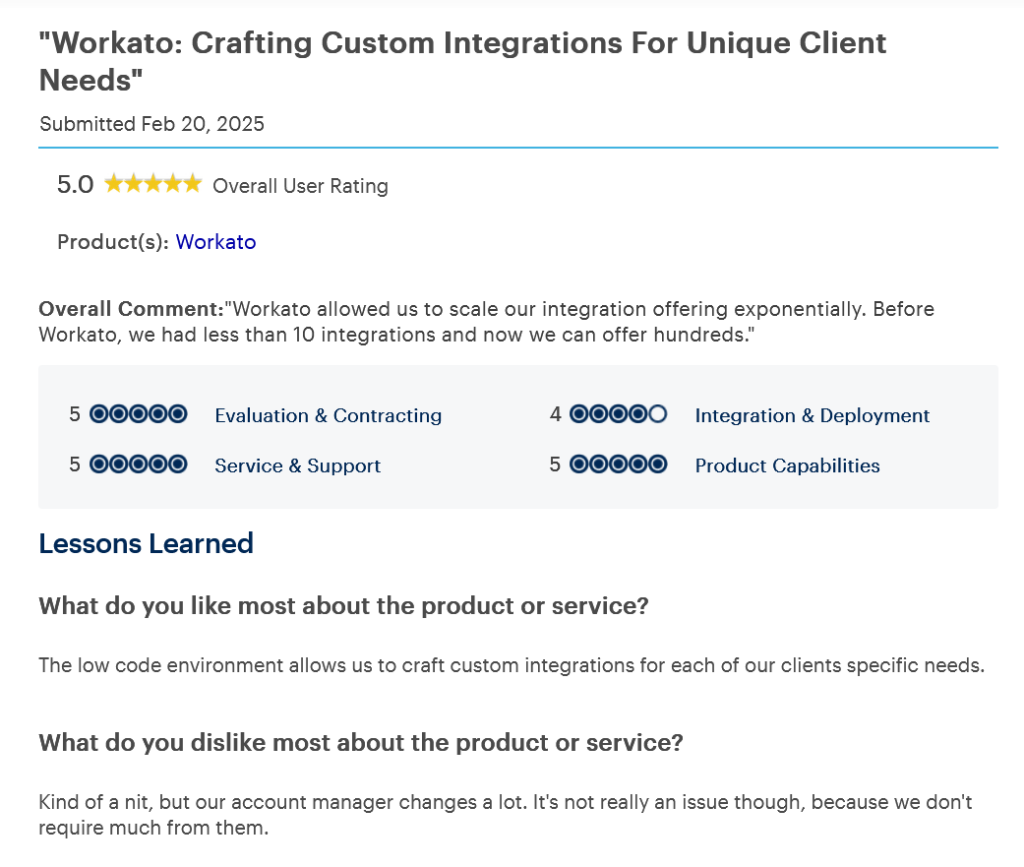
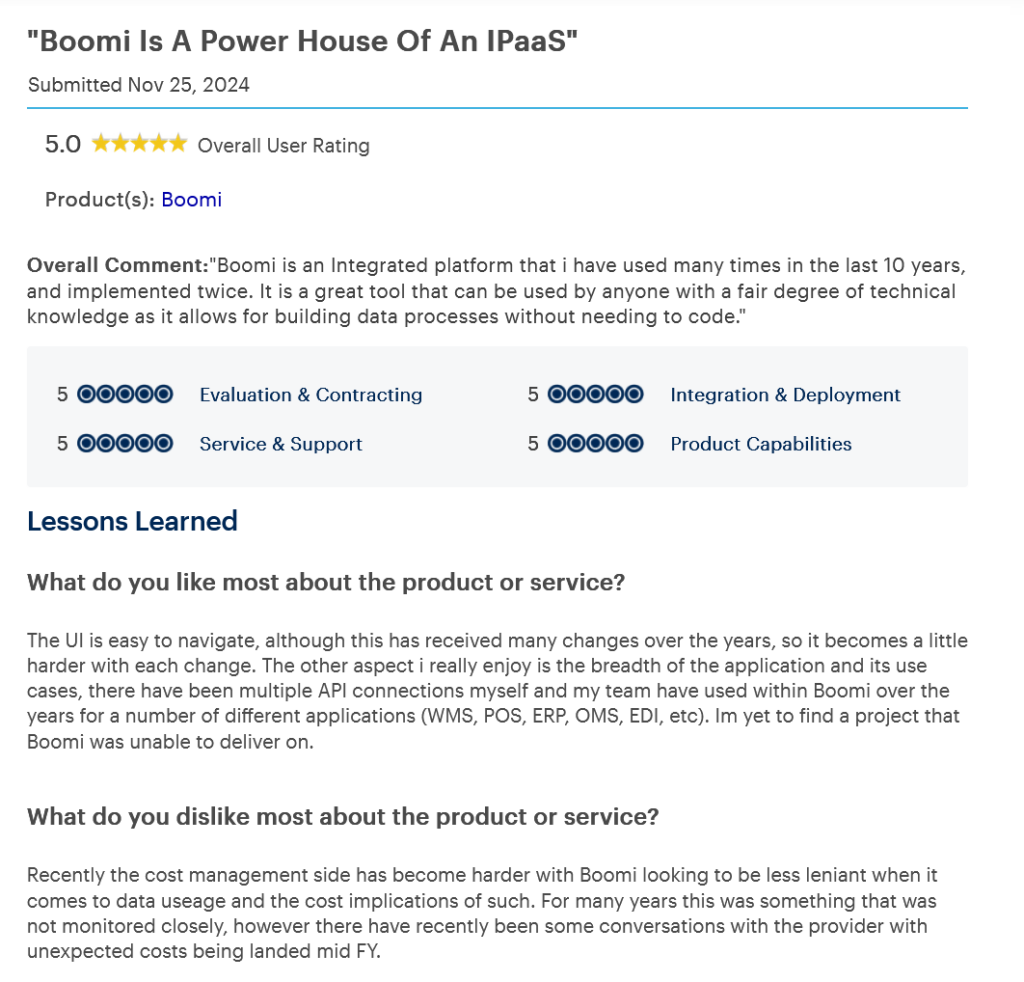
3. Boomi
Overview: Boomi is a flexible enterprise integration platform offering low-code development, API support, and high scalability. Its AtomSphere platform enables real-time data exchange between different systems using lightweight runtime engines (“Atoms”). Boomi is ideal for organizations that want to automate workflows, handle B2B/EDI transactions, and ensure seamless integration across application servers and cloud apps. Additionally, it also supports master data management (MDM) and workflow orchestration, allowing organizations to build end-to-end automation pipelines.
Advantages
- Visual, low-code builder.
- Prebuilt templates and connectors.
- API and EDI support.
- Strong scalability.
Disadvantages
- Complex cases may need certified experts.
- Performance tuning required at scale.
- Cost rises with connector use.
Best Suited For: Enterprises needing a cloud-native middleware solution with broad use cases, including API, EDI, and master data management.
4. Jitterbit
Overview: Jitterbit is a unified integration middleware platform combining API management and low-code tools. It simplifies connections between SaaS, cloud, and on-premise systems. With tools to design, deploy, and monitor application programming interfaces, Jitterbit is well-suited for companies focused on agility and speed. It supports enterprise application integration without requiring deep development resources.
Advantages
- Intuitive, low-code platform.
- API creation and monitoring.
- Fast deployment.
- Templates for common apps.
Disadvantages
- Limited connectors compared to peers.
- UI could use modernization.
- Extra effort for complex mappings.
Best Suited For: Organizations wanting to build and manage APIs and integrations quickly, with minimal development overhead.
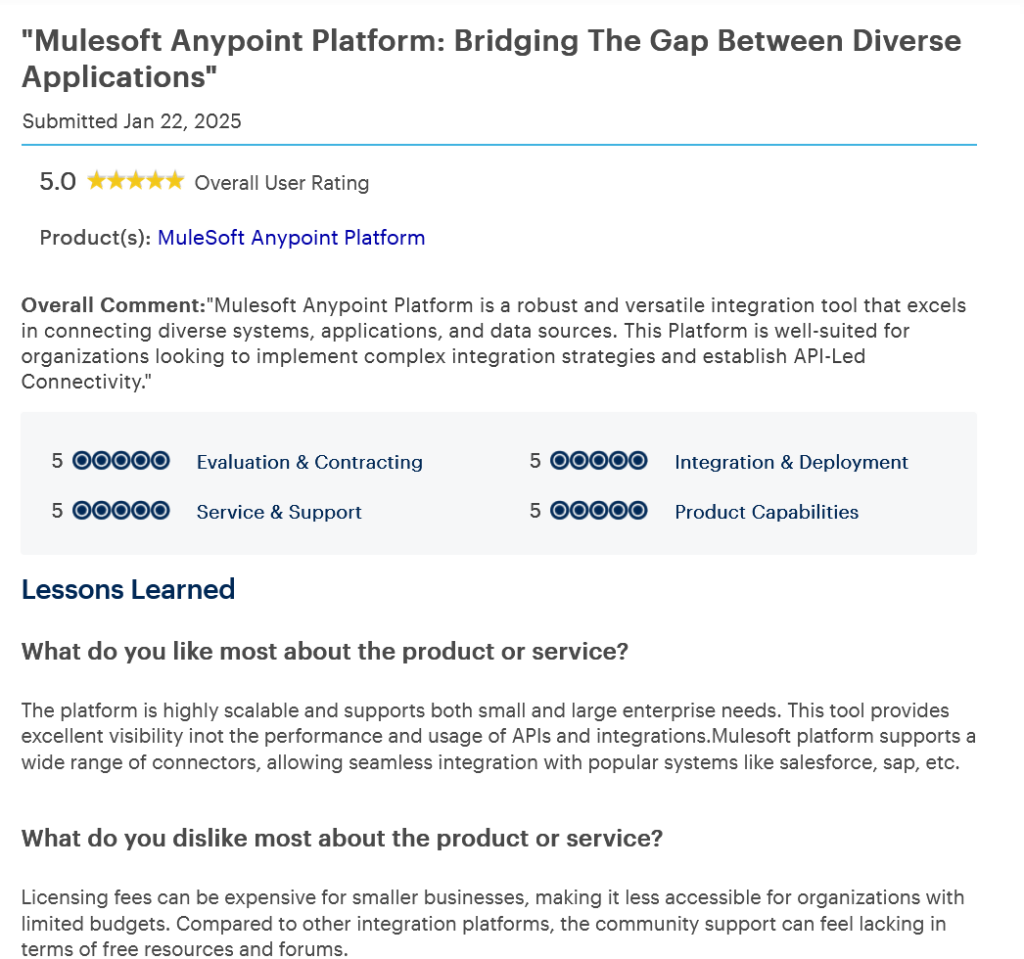
5. MuleSoft Anypoint Platform
Overview: MuleSoft’s Anypoint Platform is a top-tier Enterprise Integration Platform. Built on an API-first approach, it simplifies the integration process by allowing teams to create reusable Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). It supports high-volume data exchange and advanced security protocols. MuleSoft also provides strong Application Server support and governance capabilities, which make it well-suited for enterprises modernizing their digital core.
It includes API lifecycle management, enabling design, testing, deployment, and version control in a unified environment.
Advantages
- API-first, reusable design.
- Scales for complex, multi-system architectures.
- Robust monitoring and governance.
- Wide connector ecosystem.
Disadvantages
- High learning curve.
- Expensive licensing.
- Requires skilled developers.
Best Suited For: Large enterprises managing extensive integration processes focusing on scalable, secure API connectivity.
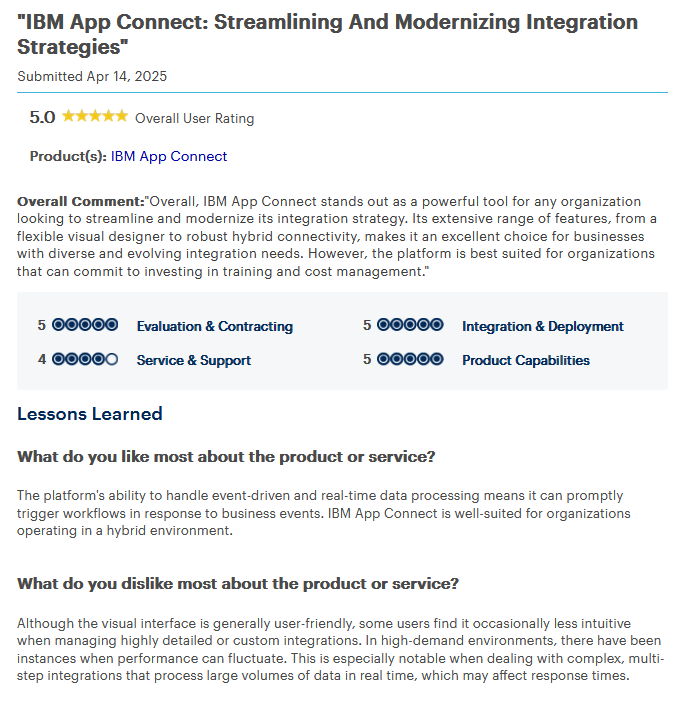
6. IBM App Connect
Overview: IBM App Connect delivers powerful middleware software for real-time data exchange across cloud, hybrid, and on-prem environments. Featuring AI-assisted mapping and a low-code UI, it supports REST, SOAP, MQ, and Message-Oriented Middleware protocols. This makes it ideal for companies looking to unify various applications and data sources. The tool integrates easily with IBM’s suite and supports Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) patterns. It also offers automatic error detection and retry capabilities to keep data flowing despite disruptions.
Advantages
- AI-enhanced mapping.
- Secure, real-time integration.
- Flexible deployment (cloud, on-prem, hybrid).
- Broad protocol and connector support.
Disadvantages
- Best for teams familiar with IBM tools.
- UI complexity.
- Pricing may limit small businesses.
Best Suited For: Enterprises managing complex workflows and diverse data sources that require scalable hybrid integration.
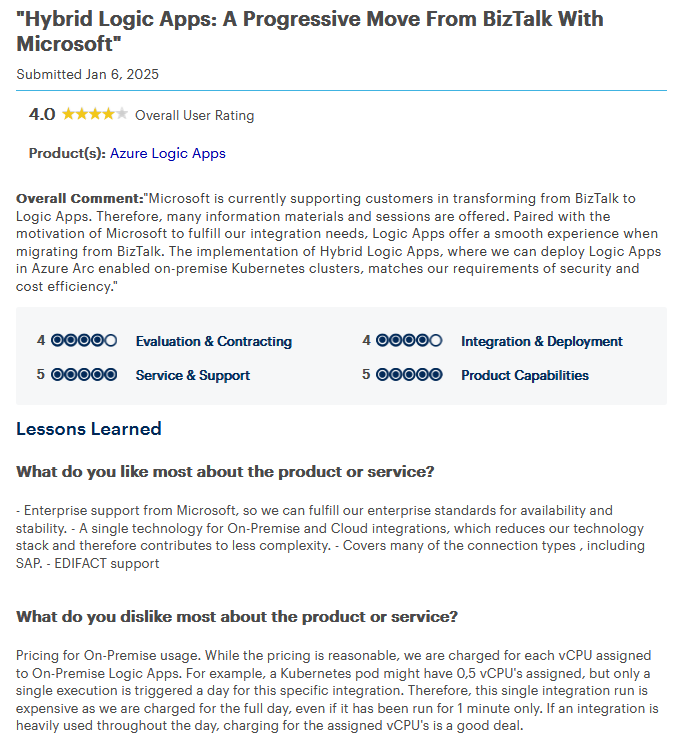
7. Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
Overview: Azure Logic Apps is cloud-first middleware software offering seamless automation through visual workflows. It is integrated well with the Microsoft stack, including Dynamics 365, Office 365, and Azure, and connects to external apps using prebuilt connectors. It enables secure data exchange across different systems while keeping operational overhead low. Azure’s built-in connectors span hundreds of services, including Salesforce, SAP, SQL Server, and social media platforms—ideal for creating wide-reaching automation.
Advantages
- Strong Microsoft product integration.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Visual workflow builder.
- Scalable for cloud-native setups.
Disadvantages
- Not ideal for non-Microsoft users.
- Limited offline/hybrid support.
- Workflow complexity affects performance.
Best Suited For: Businesses already using Azure or Microsoft services, looking for an easy way to automate business operations and connect various applications.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Middleware Integration Tool
Undeniably, your middleware integration tool puts forth a say in your businesses’ operational say and below listed are the main factors to consider while testing each integration platform:
Scalability: Consider whether the platform can grow with your business. It should handle increasing users, applications, and data volumes without adding infrastructure strain. Cloud-native tools typically offer better scalability with built-in elasticity.
Ease of Use: Look for a low-code or no-code interface that enables faster deployment and reduces dependency on IT. This is especially valuable for teams with limited technical resources.
Connector Availability: Evaluate how well the middleware supports your key systems—ERP, CRM, eCommerce, and databases. A wide range of native connectors minimizes setup time and lowers integration complexity.
Deployment Flexibility: Check if the platform supports cloud, on-premise, and hybrid environments. Flexible deployment is essential for businesses modernizing their legacy infrastructure at their own pace.
Security & Compliance: Prioritize platforms with strong security features like encryption, role-based access, and audit trails. Compliance with industry regulations should also be built in, not an afterthought.
Real-Time Sync: Real-time data exchange is critical for accurate reporting, automation, and customer experience. Middleware that only supports batch processing may limit responsiveness.
Cost Structure: Review the pricing model to ensure it fits your usage patterns. Transparent, modular pricing helps manage costs while scaling integrations over time.
Support & Community: Consistent vendor support and an active user community can significantly reduce troubleshooting time. Look for resources like live chat, forums, documentation, and implementation guidance.
Final Words
Picking the right middleware integration tool for your business might not be easy, but it is essential for efficient enterprise application integration. Integration tools streamline business operations, ensure real-time data exchange, and support growth without adding tech complexity.
When making your choice of integration solution, it is important to note that, “ One size doesn’t fit all”. Assess the integration tools based on your size, industry, and tech stack. Always remember to utilize free trials, request demos, and consider platforms that support your current and future integration needs.
Speak to our integration experts to see DCKAP Integrator can be the right fit for you.
In this Story