Rising customer demands and a changing economy can put manufacturers in a tough spot. For businesses looking to modernize, they need to begin with their ERP.
ERP integration enables centralized data flow that helps manufacturers make better decisions. This guide will provide an overview of how ERP integration enhances productivity, key benefits, best practices and key factors to consider when selecting an integration solution.
What is Manufacturing ERP Integration?
Manufacturing ERP enables business to the operations of a manufacturing process on a unified platform. While ERPs are designed to help manage verticals, businesses often opt for other systems for more specific tasks including an ecommerce platform, CRM, PIM, or EDI.
Manufacturing ERP integration allows for data to move seamlessly between these systems. It reduces the errors and costs associated with human error by automating data flow, offering real-time data, and helping make processes smoother.
Methods To Consider For Manufacturers Integrating Their ERP
There are multiple ways to integrate manufacturing ERP systems with business applications. Depending on the legacy system and IT infrastructure the integration method varies. Some of them are:
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) Integration
ESB is an architectural model that standardizes communication between systems. It enables the integration of multiple systems through a “bus-like” infrastructure. It is based on a middleware tool that translates data exchange between different systems. Due to its scalability and flexibility, ESB is the best option for large-scale manufacturers.
Cloud-Based Integration (iPaaS)
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) is a cloud-based solution connecting ERP with various applications. It relies on pre-built connectors and mapping tools to ensure fast deployment. It supports on-premise, public, and private cloud-based system integration. With real-time analytics on integration and flexibility, it reduces the reliance on the IT team.
These middleware acts as a bridge or layer between the ERP system and other applications. Here the systems are not physically connected but offer data transformation and routing capabilities. It simplifies ERP integration by providing different middleware solutions that suit your business requirements.
Custom API Integration
Custom API integration involves creating a connection between systems that specifically cater to a company’s needs. It uses Application Programming Interfaces to provide a high level of customization. It is most suited for companies with complex IT infrastructures that require more resources.
Also see: ERP Integration With Other Systems: All You Should Know
Best Practices for Integrating Manufacturing ERP Software
Effective ERP integration requires meticulous planning. Along with a dedicated team to guide the entire organization through the process. Here are 7 best practices for successful integration of manufacturing ERP.
1. Select The ERP Integration Method
Before ERP integration, assess the specific needs and requirements:
- The required bandwidth
- Identifying the data and system
- Difficulty of integration
- Identify the pain points.
- Finding the most suited ERP integration methods
2. Map Out The Integration Well
To avoid ERP integration issues, ensure that the process is planned and mapped out well. This includes finalizing intent and factoring in budgets, the teams involved, timelines, the scope of the integration and any other aspect involved. When done well, this step ensures that the integration keeps to timelines, with enough time for testing and troubleshooting, if required.
3. Train Employees & Secure Their Buy-In
It is crucial to prepare your team for smooth ERP integration and post-implementation. Start with proper training, from the operational-level employee to the top-level manager. Promote proper information flow among all departments. Provide continuous support for the company’s human resources.
4. Data Mapping And Migration
Data mapping identifies the data that needs to be transferred. Data mapping also plans its exchange and determines its end. This helps determine how data in your system correlates to the new system
Manufacturers should move only relevant data to the new system. Data migration can often pose challenges like the breaching of data. Organizations should place greater emphasis on data security and it is accessibility.
5. Develop A Testing Plan
After the data mapping, develop a plan to test the accuracy of ERP integration. This helps to identify any potential issues and troubleshoot them for operational efficiency.
- Test the new system within the team. Sandboxes can also be used in earlier stages.
- Document the conclusions for future reference and find the best solution for them.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders before making a strategic decision.
6. Evaluating And Updating the ERP System Processes
This is the post-implementation step. Gain feedback from the factory floor to the decision-makers. Track KPIs gather performance outputs, and monitor the integration for evaluation. Regularly update, monitor, and maintain the ERP software and the integration method/tool.
Why Consider Integration For Your Manufacturing ERP?
Streamlining Day-to-Day Operations
ERP integration allows for access to real-time data from various departments, streamlining the business process. Making the most of your ERP via integration helps reduces production delays, and improves inter-departmental cooperation.
Enhancing Data Accuracy
Manual data entry is very prone to errors. Messing up the bill of materials can disrupt business operations. ERP integration helps get rid of outdated manual processes to ensure data accuracy.
Real-Time Data Analysis
Integration helps ensure access to real-time insights that are crucial to track the KPI metrics and look over the performance. This allows you to keep an eye on inventory management and to strategize based on data-backed decisions.
Cost Benefits
Manufacturing ERP integration enables better resource allocation and access to accurate data. The byproduct of all this is better financial management. With real-time insight into operations, it can reduce any costly errors and customer churn.
Here Are Some Common Integration Challenges Worth Paying Attention To
Security Risks
ERP integration involves migrating valuable business data, causing significant data security risks. Any breach of data during data exchange can be colossal to the business. Thus, security strategies like multi-factor authentication and conducting security audits are mandatory.
Technical Challenge
Companies use a plethora of hardware and software tools for their operations. Integrating these different types into an ERP system can pose some technical dilemmas. For businesses with the resources this can be handled internally, but others can seek the support of reliable vendors or integration experts.
Resistance From Teams Or Stakeholders
ERP integration calls for a drastic shift in work dynamics. As more departmental information gets centralized, the workflow changes. Employees may have the fear of adjusting to new technology. To overcome the fear, provide necessary training and resolve their queries.
Similarly, if stakeholders are not on board, the ERP integration may be delayed, often disrupting business operations. Before moving with the plan, ensure the interested parties are on the same page.
Data Consistency
Data maintained in different systems by different teams can run into issues with data consistency. This is exacerbated in companies that rely on tribal knowledge held by a few. Ensuring data consistency can help speed up the integration process.
| 💡 The DCKAP Integrator is equipped with robust advanced data mapping and modifying features. These allow businesses to easily sync data from one system to the other. |
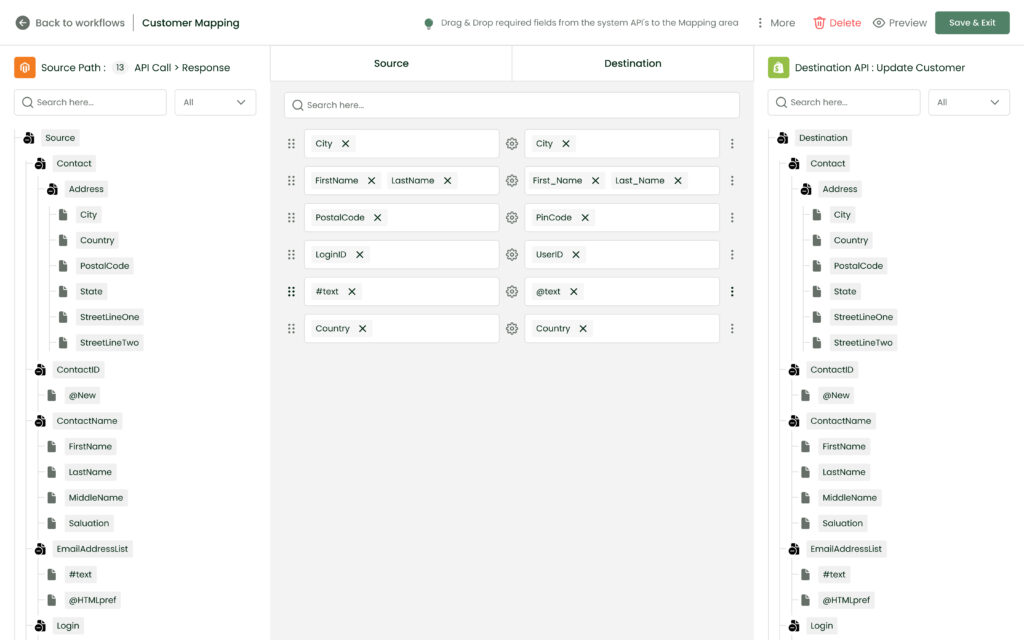
DCKAP Integrator: The ERP Integration Platform For Manufacturers & Distributors
With changing demographies, and more businesses leveraging tech for their operations, integrating manufacturing ERP has become the need of the hour to remain competitive. Ensuring your sales, customer success, logistics, account servicing teams all have access to real-time information is vital.
Built for manufacturers and distributors, the DCKAP Integrator facilitates seamless syncing of data between third-party apps to ERP systems. It ensures smooth integration with ERP software like your ecommerce platform, PIM, CRM, marketplace, and more.
From cloud-based systems to on-premise, any app can connect. The easy-to-use interface simplifies the integration process saving you time and cost.
DCKAP Integrator is also backed by a team of experts, ready to customize the integrations for any specific business requirements that you may need.
Schedule a demo with our integration experts today, or learn more about the right plan for you.
FAQs
How does ERP integration work?
ERP integration works by merging various software in a system into a unified space. ERP is a centralized system that streamlines the information flow with real-time insights. ERP integration is a very complex process that requires careful planning and evaluation.
How do manufacturers use ERP systems?
Manufacturers use ERP systems to collect, analyze, and unify their operational data. Leading to easy information access across all departments. ERP systems provide real-time data, improving data accuracy. Allowing manufacturers to identify any errors before they snowball into disrupting the business.
Why is ERP integration necessary for manufacturers?
Enterprise Resource Planning software plays a key role in enhancing operational efficiency. In the manufacturing business, it optimizes resource allocation and ensures quality assurance. This improves the supply chain management and the entire business’s efficiency.
Contents