Acumatica is a powerful and popular cloud-based ERP solution designed to help businesses streamline their operations across finance, inventory, sales, and more. When integrated with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), Acumatica becomes even more efficient by automating tasks that would otherwise require manual effort.
Acumatica EDI Integration enables the electronic exchange of critical business documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, directly between Acumatica ERP and your trading partners’ systems. Let’s see how this works.
Methods of Acumatica EDI Integration
Technically, ERP EDI integration methods can be categorized into three broad types: direct integration, indirect integration, and hybrid integration. However, when it comes to Acumatica EDI integration, there isn’t enough evidence to support the widespread use of all these methods. Instead, two of the most popular and practical approaches are typically used: Embedded EDI (direct integration) and iPaaS Integration (indirect integration).
1. Embedded EDI
Embedded EDI is a straightforward yet distinct approach that provides seamless connectivity for managing trading partner relationships. Think of it as being very similar to native integration but with a few key differences.
In the context of the Acumatica platform, SPS Commerce is an EDI provider that serves as an embedded or built-in EDI solution. It is fully integrated into the Acumatica ecosystem, delivering all the tools and support needed to manage EDI processes efficiently. From initial implementation to everyday operations, SPS Commerce offers:
- Proven EDI technology.
- Ongoing support to guide clients throughout the process.
However, it’s important to note that SPS Commerce is not directly tied to Acumatica as a brand. This distinction prevents it from being classified as a native integration, even though it works seamlessly within the platform.
Considerations for Users:
- Some users report that expert support from SPS Commerce may fall short of expectations.
- Licensing fees are often higher compared to alternative solutions.
Despite these concerns, Embedded EDI with SPS Commerce is a solid option for companies looking for comprehensive EDI capabilities within Acumatica.
2. Middleware Integration
iPaaS or Middleware Integration is another widely used method for EDI integration with Acumatica. This approach leverages third-party tools that act as intermediaries to manage EDI operations effectively.
The most popular middleware tool for Acumatica EDI integration is TrueCommerce. Interestingly, Acumatica Cloud ERP originally relied on B2B Gateway for EDI solutions. However, in 2020, TrueCommerce acquired B2B Gateway, making TrueCommerce a key player in this role.
Another excellent alternative to TrueCommerce is the DCKAP Integrator. This tool stands out for its expertise in integrating a variety of ERP systems, including those used by manufacturers and distributors. With a team of knowledgeable EDI experts, DCKAP Integrator is well-equipped to handle diverse integration requirements for different business needs.
Also read: Understanding QuickBooks EDI Integration [Methods + Types + Top Tool]
| Additional Information: How TrueCommerce Differs From DCKAP Integrator Both TrueCommerce and DCKAP Integrator are fully managed services, but they differ slightly in their approach to EDI processes: TrueCommerce: Utilizes B2B Gateway for EDI transmission and translation. Handles the integration process while outsourcing key EDI tasks to the B2B Gateway. DCKAP Integrator: Uses MFT Gateway as a pathway for EDI transactions. Manages both the integration and EDI translation in-house, without relying on external translation solutions. This difference in architecture does not significantly impact day-to-day operations but provides insight into how these tools manage the EDI lifecycle. For businesses seeking a middleware solution, both TrueCommerce and DCKAP Integrator are reliable options with robust support and functionality. The choice between them may depend on specific preferences regarding EDI transmission and translation workflows. |
Understanding The Flow Of Acumatica EDI Transactions
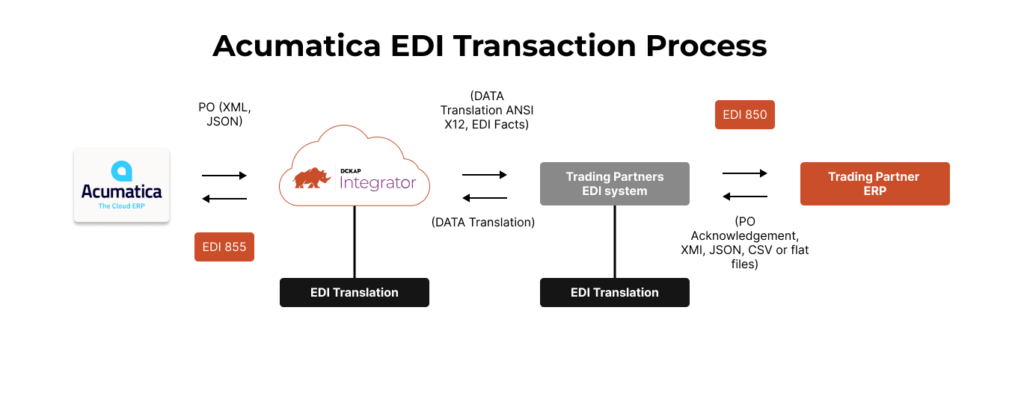
Here’s a breakdown of the entire Acumatica EDI integration process in a more simplified manner:
From Acumatica to the Middleware Tool (DCKAP Integrator):
When you generate a purchase order in Acumatica system, it is not in an EDI format. Acumatica creates the data in its native format (e.g., JSON, XML, or flat files). The middleware tool, in this case, DCKAP Integrator, translates this native format into an EDI 850 (Purchase Order), ensuring it adheres to the specific EDI standards required by the seller (e.g., ANSI X12 or EDIFACT).
From the Middleware Tool to the Seller’s System:
Once the EDI 850 is created, the middleware transmits it using the appropriate communication protocol (e.g., AS2, FTP) to the seller’s system. Additional formatting is applied only if the seller’s system requires further tweaks.
Seller’s Internal System Generates the Response Document:
When the seller receives the purchase order, their ERP or internal system generates response documents like order acknowledgments, shipping notices, or invoices in its preferred internal format (e.g., XML, JSON, flat files, or CSV). These formats are not EDI-compliant.
Seller’s EDI Solution Translates the Document:
The seller’s EDI translation tool converts these internal formats into the required EDI standard (e.g., ANSI X12 or EDIFACT). The resulting EDI documents, such as EDI 855 (Order Acknowledgement), EDI 856 (Advance Shipping Notice), or EDI 810 (Invoice), are then sent to the middleware tool (DCKAP Integrator).
Middleware Tool Processes the EDI Document:
When the middleware receives the EDI document from the seller, it performs the following tasks:
- Compliance Checks: Ensures the document adheres to the required EDI standards and any specific trading partner guidelines.
- Translation to Acumatica-Compatible Format: Converts the EDI file into a format that Acumatica solution can understand, such as XML or JSON.
This streamlined process ensures accurate and automated data exchange between Acumatica and the trading partner’s system, reducing manual errors and improving operational efficiency.
Common Transaction Sets in Acumatica EDI Integration
Acumatica EDI integration supports a wide range of transaction sets that facilitate seamless communication between trading partners. These transaction sets are standard EDI documents that automate various business processes. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
- EDI 850 – Purchase Order:
Sent by the buyer (e.g., a distributor) to the seller to request goods or services. It contains details such as product descriptions, quantities, prices, and delivery dates. - EDI 855 – Purchase Order Acknowledgment:
Sent by the seller to confirm receipt of a purchase order and provide details about the order’s acceptance, modifications, or rejection. - EDI 856 – Advance Shipping Notice (ASN):
Sent by the seller to inform the buyer about a shipment’s details, including the contents, packaging, and expected delivery date. - EDI 846 – Inventory Inquiry/Advice:
Used by sellers or suppliers to provide buyers with real-time inventory levels, helping manage stock and avoid shortages. - EDI 810 – Invoice:
Sent by the seller to the buyer as a request for payment. It includes details of the goods or services provided, their costs, and payment terms. - EDI 870 – Order Status Report:
Provides updates about the status of an order, including whether it has been shipped, delayed, or partially fulfilled. - EDI 940 – Warehouse Shipping Order:
Used to instruct a warehouse to ship goods to a specific location, including detailed shipping and packing instructions. - EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgment:
A confirmation document sent to acknowledge the receipt of an EDI transaction, ensuring that the communication was successful.
Also read: Epicor EDI Integration Explained
Benefits Of Acumatica EDI Integration
Here are the top advantages you can get by integrating EDI with Acumatica ERP:
- Faster Order Processing: Automate repetitive tasks like generating purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices. This speeds up the order-to-cash and procure-to-pay cycles.
- Fewer Manual Errors: Eliminate manual data entry. Reduce human errors in orders, invoices, and shipping details, which saves time and avoids costly mistakes.
- Better Communication with Trading Partners: Exchange data with suppliers, retailers, or manufacturers in real-time. This ensures quick responses and smoother collaboration.
- Cost Savings: Cut costs by reducing paperwork, postage, and administrative overhead. Use your team’s time more efficiently by focusing on higher-value tasks.
- Improved Inventory Management: Keep track of inventory levels with real-time data. Avoid stockouts or overstock situations by syncing supply and demand data seamlessly.
- Compliance with Trading Partner Requirements: Many large retailers and partners require EDI for doing business. Meeting their standards helps you maintain and grow partnerships.
- Scalability: With future business growth, EDI makes it easier to handle higher order volumes and work with more trading partners.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Deliver goods faster, improve accuracy, and stay responsive. This builds trust and loyalty with customers.
- Real-Time Visibility: Track orders, shipments, and payments as they happen. Make better decisions with up-to-date information at your fingertips.
- Standardized Data Exchange: Communicate in a consistent format, regardless of the systems used by your trading partners. This ensures successful integration with multiple partners.
Also read: B2B EDI Integration Explained [+Top Solution for Distributors]
Challenges and Best Practices for Acumatica EDI Integration
Complex Data Mapping:
- Challenge: Mapping data between Acumatica’s internal format and the EDI standards can be complicated, especially with customized partner requirements.
- Solution: Use a robust integration tool like DCKAP Integrator, which simplifies mapping and adapts to trading partner-specific configurations.
Compliance Issues:
- Challenge: Different trading partners may follow unique EDI standards or guidelines, increasing the risk of non-compliance.
- Solution: Perform thorough compliance checks using middleware tools that validate documents before sending or receiving them.
Error Handling:
- Challenge: Errors like missing data fields or incorrect document formatting can disrupt the transaction flow.
- Solution: See if your middleware tool has the capability of automated error detection and alerts to flag and resolve issues quickly.
Communication Protocols:
- Challenge: Partners may use different communication protocols (e.g., AS2, SFTP, VANs), requiring seamless connectivity.
- Solution: Choose an integration platform that supports multiple protocols and ensures secure data transmission.
Change Management:
- Challenge: EDI requirements or business operations may change over time, requiring ongoing updates.
- Solution: Work with a flexible integration partner or tool that can adapt to these changes without disrupting operations.
Onboarding New Trading Partners:
- Challenge: Integrating with new trading partners can be time-consuming and error-prone.
- Solution: Use a scalable integration tool to quickly configure new partner connections without manual rework.
Lack of Internal EDI Expertise:
- Challenge: Your team may not have in-depth knowledge of EDI standards and integration processes.
- Solution: Partner with experienced EDI providers like DCKAP Integrator, which offers expert support throughout the implementation process.
Top Integration Tool For Manufacturers And Distributors – DCKAP Integrator
DCKAP Integrator is a cloud-based integration solution built for manufacturers and distributors. It’s designed to solve their unique challenges and simplify ERP EDI integration. This tool has extensive experience in working with B2B businesses which is why it understands what businesses need. It has worked with all types of ERP systems, making it an ideal solution in this space.
Here’s the best part: DCKAP Integrator handles everything from start to finish. You don’t need separate tools for EDI translation or additional software for compliance. It’s a fully managed service that takes care of all EDI processes, including data mapping, translation, communication, and monitoring.
This means you can focus on your business without worrying about integration headaches. Just communicate your needs, and DCKAP Integrator will manage the rest. It ensures a hassle-free setup, smooth operations, and seamless data exchange between your systems and trading partners. Get in touch with us today to see how DCKAP Integrator can help!
FAQs
What is EDI integration?
EDI integration is the process of connecting an organization’s internal systems, like ERP or accounting software, with its trading partners’ systems to exchange business documents electronically. This integration ensures seamless communication, automates data exchange, and eliminates manual processes. It enables businesses to send and receive purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other documents efficiently and in real-time.
What is EDI API integration?
EDI API integration combines traditional EDI functionalities with modern API capabilities. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow systems to communicate directly and exchange data, while EDI ensures compliance with specific standards and formats. Businesses can use APIs to connect with an EDI translator tool, enabling real-time data exchange between trading partners. However, APIs alone don’t offer full EDI integration, as they lack automation and require significant technical expertise.
Is API integration possible for EDI to integrate with Acumatica?
APIs can create a bridge between your system and an EDI translator tool, facilitating data exchange with your trading partners.
However, the process involves hours of manual work. Each time you need to send or receive an order, you’ll have to manually trigger the process.
There’s no automation to handle recurring transactions or real-time updates. It’s not suitable for businesses with limited knowledge of EDI or lacking a dedicated technical team. Also, keep in mind that each connection with a trading partner is built from scratch which is why it is not ideal if you want to connect your system with a network of trading partners.
What are EDI standards and formats?
EDI standards are predefined rules that dictate the structure and content of EDI documents to ensure uniformity across systems. Common standards include ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and TRADACOMS. EDI formats, such as 850 (Purchase Order), 810 (Invoice), and 856 (Advance Shipping Notice), specify the type of transaction being conducted. These standards and formats ensure smooth communication and compatibility between different trading partners and systems.
Is API replacing EDI?
While APIs are gaining popularity, they are not replacing EDI entirely. APIs offer flexibility and real-time data exchange, making them suitable for some modern use cases. However, EDI remains the standard for B2B transactions due to its reliability, scalability, and adherence to industry standards. In many cases, businesses use a combination of EDI and API technologies to leverage the strengths of both.
What is the best Acumatica EDI solution for the manufacturing and distribution industry?
For manufacturers and distributors, DCKAP Integrator is the most complete way to achieve seamless EDI integration with Acumatica. Designed to meet industry standards, it addresses the unique challenges of managing large order volumes, real-time inventory updates, and maintaining compliance with trading partner requirements. As an industry leader, DCKAP Integrator simplifies complex processes, automates repetitive tasks, and ensures real-time visibility across the supply chain. Its focus on continuous improvement makes it an exceptional EDI system for B2B businesses striving for efficiency and reliability.
Contents




